Degradation of Pyrimidine Nucleotides
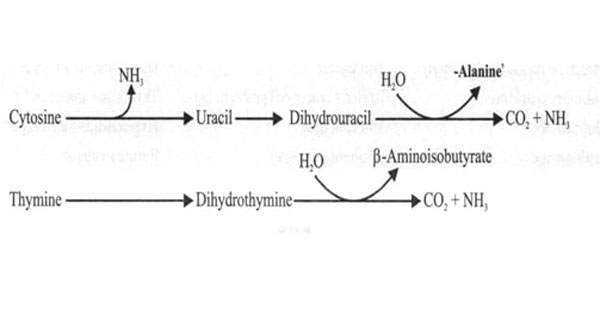
Degradation of Pyrimidine Nucleotides CATABOLISM OF PYRIMIDINE NUCLEOTIDES Cytosine and Uracil to Beta Alanine — CO2, NH3 Thymine and β- aminoisobutyrate — CO2, NH3 The end products are highly water soluble. Exam Important The end products of pyrimidine catabolism are highly water soluble. E.g. CO2, NH3, β- aminoisobutyrate, beta alanine. Pseudouridine is excreted unchanged as […]
Degradation of Pyrimidine Nucleotides Read More »