COLLE’S FRACTURE
COLLE’S FRACTURE
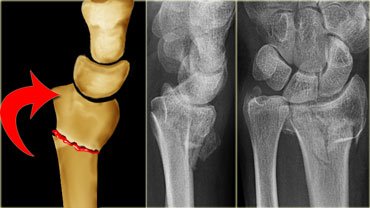
- Defined as transverse fracture of the distal radius.
- Just above the wrist at the level of cortico-cancellous junction, with dorsal displacement of distal fragment.
- Mechanism of injury : fall on out-stretch hand

- It is the most common osteoporotic-related fracture in the upper limb.
- Hence, it is common among post-menopausal women.
Clinical features

- Pain, swelling, deformity.
- Palpation over distal radius : tenderness and irregularity.
- Dinner fork deformity.
- Radial styloid being leveled or situated proximal to the ulnar styloid.

Complications
1) Joint stiffness
- Involving the fingers, wrist, elbow and shoulder.
2) Mal-union
- Occurs usually unnoticed within the immobilisation cast.
3) Subluxation of the distal radio-ulnar joint
- Resulting shortening of the radius, which made the ulnar styloid more prominent.
- Hence, any movement of the wrist joint involving pronation/supination or ulnar deviation is restricted or is painful.
4) Carpal tunnel syndrome
5) Ruptured tendon of extensor policis longus
6) Sudeck’s osteodystrophy
- Colles’ fracture is the commonest cause of this condition in the upper limb.
- Characterised by pain, swelling of wrist, hand and fingers, and deformity.
- There’s diffuse tenderness, and the skin over it appears glazed, stretched.
- Treated by physiotherapy.
Treatment
1) Undisplaced
- Cast immobilisation for 6 weeks, applied below elbow towards the neck of metacarpals.
- Hand is immobilised in functional position, with slight palmar flexion and ulnar deviation.
2) Displaced (with dinner fork deformity)
- First, close manipulative reduction is done under anesthesia.
- Ask your assistant to apply traction over the wrist joint by holding the patient’s hand, and counter traction at the elbow joint.
- Press over the dorsal aspect of deformity, at the same time try palmar-flexing, ulnar deviation, and pronating the hand.
- After reduction, confirm that it’s properly done by X ray.
- Apply colles’ cast.
3) Comminuted
- Requires open reduction and internal fixation.
Exam Important
- Colles fracture best describes the patient’s wrist fracture.
- Colles fracture is fracture at cortico-cancellous junction of the distal end of the radius with dorsal tilt.
- Deformities present in colles fracture is Dorsalt tilt.
- Colles fracture is common in women because of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
- Colles fracture is common in old age.
- Dinner fork deformity is the characteristic of colles fracture.
- Proximal impaction , Lateral rotation & Dorsal angulation is seen in colles fracture.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome, Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), Frozen hand shoulder syndrome are the complications of Malunited Colles fracture.
- Stiffness of wrist, Stiffness of shoulder & Carpal tunnel syndrome are complication of colles fracture.
Don’t Forget to Solve all the previous Year Question asked on COLLE’S FRACTURE
Click Here to Start Quiz
Click Here to Start Quiz
