Cryptococcus neoformans
Cryptococcus neoformans
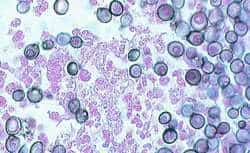
- Opportunistic fungal pathogen
Most common cause of fungal meningitis:
- In immuno-compromised patients (such as people with AIDS).
Morphology
- Cell wall is gram-positive.
- Yeast with prominent polysaccharide capsule.
- Unicellular

Important features
- Possess urease.
- It reproduces by budding
- Single buds are characteristically narrow at the base.
- It does not produce pseudohyphae
Serotypes
- Four capsular serotypes – A, B, C and D
- Most infections in immunocompromised patients are caused by serotype A.
Abundant in pigeon droppings :
- Contain serotype A and D.
- Eucalyptus tree contains serotype B.
Culture:
- Colonies develop within a few days on most media
- Sabouraud’s dextrose agar
- Other culture media are Blood Agar, BHI Agar, Bird seed agar etc.
Temp:
- Room temperature or 37 °C.
- Colonies in SDA are creamy, white and mucoid (because of capsule)
- Cryptococcus neoformans is sensitive to cycloheximide
Pathogenesis
- Infection is initiated by inhalation of the yeast cells.
- Cryptococcus has predilection for lung and meningis.
- The primary pulmonary infection may be asymptomatic .
- In immune-compromised patients with impaired T cell immunity, the yeasts may multiply
- Disseminate to other parts of the body
- But preferentially to the central nervous system (neurotropic), causing cryptococcal meningitis.
- Other common sites of dissemination include the skin, adrenals, bone, eye and prostate gland.
Virulence Factors of Cryptococcus neformans
Capsule:
- Anti-phagocytic
- Protection under drying condition
- Ideal size range for alveolar deposition
Phenoloxidase:
- Responsible for melanin production
- Melanin might act as a virulence factor by making the organism resistant to leukocytes attack.
Exam Important
Cryptococcus neoformans
Most common cause of fungal meningitis:
- In immuno-compromised patients (such as people with AIDS).
Morphology
- Yeast with prominent polysaccharide capsule.
- Unicellular
- Possess urease.
- It reproduces by budding
- It does not produce pseudohyphae
Serotypes
- Four capsular serotypes – A, B, C and D
Abundant in pigeon droppings :
- Contain serotype A and D.
- Eucalyptus tree contains serotype B.
Culture:
- Sabouraud’s dextrose agar
Temp:
- Room temperature or 37 °C.
Pathogenesis
- Cryptococcus has predilection for lung and meningis.
Virulence Factors of Cryptococcus neformans
Capsule:
- Anti-phagocytic
Phenoloxidase:
Don’t Forget to Solve all the previous Year Question asked on Cryptococcus neoformans
Click Here to Start Quiz
Click Here to Start Quiz
