FLAPS
FLAPS
- Flap is a piece of tissue (skin or subcutaneous fat) transferred from donor to recipient area along with its vascularity.
- Parts of flap-
- Base
- Pedicle
- Tip
Indications-
- To cover defects forward where free skin graft cannot be used as exposed base bone, bare tendons, base cartilage.
- Wounds with exposed joints, exposed major vessels & nerves.
- Implant exposure
- In wounds with soft tissue loss
- Breast restruction following mastectomy.
- Skin flap is used in bone, tendon and cartilage.
Classification of Flaps-
According to proximity of the wound-
a) Local flap-
- Shares a side with the wound.
- For small defects

b) Distant flaps-
- Away from defects when tissue cannot cover the defect & a flap is required.
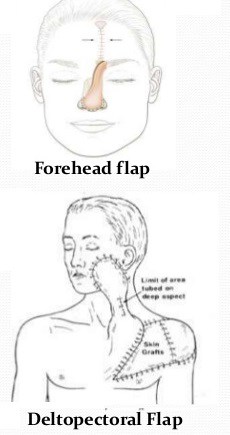
- E.g.- Forehead, deltopectoral, groin, Latissimus dorsi muscle flap (breast reconstruction), Pectoralis major flap (mandibular reconstruction), transverse rectus abdominis flap- TRAM (breast reconstruction).
c) Free flap-
- Tissue transferred to another site.

According to method of transfer (geometric design)
i) Transposition- reconstruction of facial skin defect
a) Z plasty- for pilonidal sinus, lengthening scars

b) Rotational flap- for gluteal region, scalp, buttocks, deltoid area

c) Rhomboidal flap- cheek, temporal, back & flat surface defects

Advancement flaps-
a) V-Y advancement flap- E.g.- finger tips, extremities

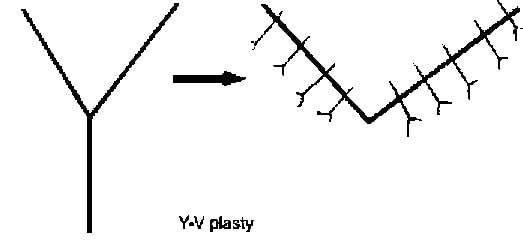
b) Y- V advancement
c) Bipedicle advancement flaps- E.g. Lower eyelid

According to blood supply-
a) Random pattern flap-
- For small, full thickness defects.
- Based on dermal & sub dermal plexus
- Length to breadth- 1.5:1 (limited)
E.g. Cross finger flap

b) Axial pattern flap-
- Based on direct cutaneous vessels
- Longer flaps with known vessels supplying
- Develops as island flaps as flap mobility
E.g. Deltopectoral flap, groin flap

c) Myocutaneous flap-
- Muscle along with overlying skin
- Useful in covering bare bone.
E.g. Pectoralis major flap
d) Fasciocutaneous flap-
- Consists of deep fascia along with overlying skin
E.g. Forehead flap, deltopectoral flap

According to composition of tissue-
i) Simple flaps- consist of single tissue
- Cutaneous flaps- skin- skin flaps
- Fascia flaps- only fascia
- Muscle flaps- only muscle
ii) Composite flaps– more than one type of tissue
- Musculocutaneous
- Osteocutaneous
- Fasciocutaneous

Exam Important
a) Local flap-
- Shares a side with the wound.
- For small defects
b) Distant flaps-
- Away from defects when tissue cannot cover the defect & a flap is required.
E.g.- Forehead, deltopectoral, groin, Latissimus dorsi muscle flap (breast reconstruction), Pectoralis major flap (mandibular reconstruction), transverse rectus abdominis flap.
c) Free flap-
- Tissue transferred to another site.
i) Transposition- reconstruction of facial skin defect
a) Z plasty- for pilonidal sinus, lengthening scars

b) Rotational flap- for gluteal region, scalp, buttocks, deltoid area

c) Rhomboidal flap- cheek, temporal, back & flat surface defects

ii) Advancement flaps-
a) V-Y advancement flap- E.g.- finger tips, extremities

b) Y- V advancement

c) Bipedicle advancement flaps- E.g. Lower eyelid
III) According to blood supply-
a) Random pattern flap-
- For small, full thickness defects.
- Based on dermal & sub dermal plexus
- Length to breadth- 1.5:1 (limited)
E.g. Cross finger flap

b) Axial pattern flap-
- Based on direct cutaneous vessels
- Longer flaps with known vessels supplying
- Develops as island flaps as flap mobility
E.g. Deltopectoral flap, groin flap

c) Myocutaneous flap-
- Muscle along with overlying skin
- Useful in covering bare bone.
E.g. Pectoralis major flap
d) Fasciocutaneous flap-
- Consists of deep fascia along with overlying skin
E.g. Forehead flap, deltopectoral flap
Click Here to Start Quiz
