MYCOTIC CORNEAL ULCER
MYCOTIC CORNEAL ULCER
- The incidence of corneal ulceration due to fungi has increased significantly due to long-term unwarranted use of antibiotic & steroid.
- The m/c mode of infection is injury by vegetative material such as crop leaf, thorn, wooden stick.
- The causative fungus are Aspergillus fumigates (most common), Candida albicans & fusarium.
Clinical features
- Symptoms are similar to bacterial corneal ulcer.
- In general they are less marked than the equal sized bacterial ulcer.
- Signs are very prominent i.e signs are more prominent than symptoms.
- Following signs can be seen:
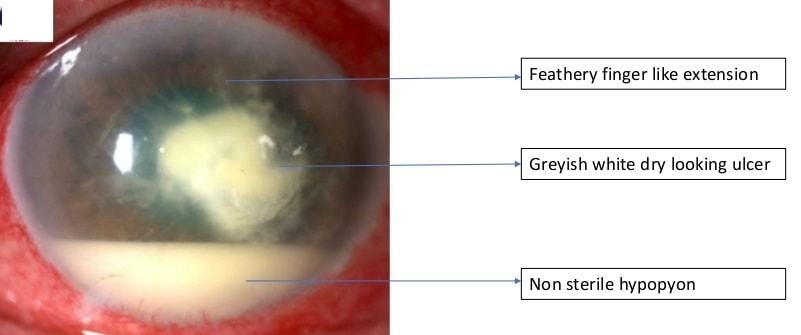
- Grayish-white dry looking ulcer with the elevated rolled out feathery & hyphate margins.
- Feathery finger-like extension into surrounding stroma under intact epithelium.
- A sterile immune ring (yellow line) of Wesseley.
- Multiple small satellite lesions
- Non –sterile (infected) hypopyon (Pseudohypopyon)
- Perforation is rare & corneal vascularisation is conspicuously absent


Diagnosis
- Examination of wet KOH will show:
- Filamentous fungi (branched septate hyphae): Aspergillus fumigates, Fusarium
- Non-filamentous (yeast like fungi): Candida
Treatment
- Treatment of corneal fungal ulcer involves:
1. SPECIFIC (DEFINITIVE): Includes antifungal drugs.
A) Topical antifungals
i) For filamentous fungi (Aspergillus fusarium):
- Natamycin (5%) eye drops (drug of choice)
- Miconazole ointment
- Amphoterecin B drops
ii) For yeast (Candida):
- Amphhoterecin B (Drug of choice)
- Nystatin
B) Systemic antifungals
- May be required in severe cases.
- Fluconazole or ketoconazole may be used
2. ADJUNCTIVE/ CONCURRENT:
- Cycloplegics (1% atropine ointment or drop is the DOC) should be used to:
- Reduce pain from ciliary spasm
- Prevent posterior synaechiae
- Reduce uveal inflammation
- Topical steroids enhance fungal replication & corneal invasion & are contraindicated during early therapy of a fungal corneal ulcer.
Exam Important
- Features of fungal ulcer is Dry ulcer.
- Hypopyon in a fungal corneal ulcer contains Fungal filaments.
- Common fungus causing corneal ulcer is Aspergillus fumigates, Candida albicans & fusarium.
- Immune ring is a feature of Fungal corneal ulcer.
- Satellite lesions in the cornea may be seen in Fungal corneal ulcer.
- Natamycin is the drug of choice for treatment of corneal ulcers caused by filamentous fungi.
- Atropine sulphate eye ointment is the most important adjuvant therapy in a case of fungal corneal ulcer.
- Steroid is contraindicated in Fungal corneal ulcer.
Don’t Forget to Solve all the previous Year Question asked on MYCOTIC (FUNGAL) CORNEAL ULCER

