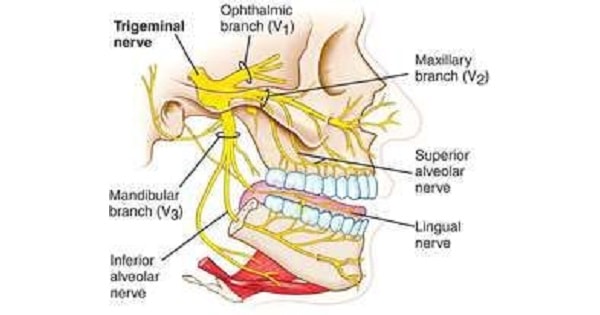
TRIGEMINAL (V) NERVE
INTRODUCTION:
- Largest cranial nerve, passes through Meckel’s cave.
- Derived from 1st pharyngeal arch.
- Mixed nerve (sensory component is more prominent).
- Large sensory root: carries sensation from the skin and mucosa of most of the head.
- Smaller motor root: innervates most of the masticatory muscles (masseter, temporalis, pterygoids, mylohyoid), and the tensor tympani muscle of the middle ear.
- The efferent fibers originate in the motor nucleus of V in the pons and controls the muscles involved in mastication
- The sensory root (the main portion of the nerve) arises from cells in the semilunar ganglion (also known as the Gasserian, or trigeminal, ganglion) in a pocket of dura (Meckel’s cavity) lateral to the cavernous sinus.
NUCLEI OF TRIGEMINAL NERVE:
1. General somatic afferent:
- These sensory fibers arise from ‘pseudounipolar neurons’ of trigeminal ganglion.
- These fibers terminate in three sensory nuclei of trigeminal:
a. Main (principal) sensory nuclei (superior sensory nucleus):
- Recieves sensory fibres of fine touch & pressure from face.
b. Spinal nuclei (sensory in upper pons to C2 segment of spinal cord):
- Recieves sensory fibers of pain & temperature from face.
- Also recieves sensory inputs (general somatic afferents) from facial nerve (skin of ear), Glossopharyngeal (middle ear), & auricular branch of Vagus (skin of ear).
c. Mesencephalic nuclei (sensory in midbrain):
- Recieves proprioceptive fibers from muscle of mastication & TMJ.
- Also recieves proprioceptive inputs by inputs III, IV, VI cranial nerves (from extraocular muscles) IX nerve (from Stylopharangeus); VII nerve (from facial muscles); & from XII nerve (from muscles of tongue).
2. Special visceral efferent (branchial efferent):
- for muscles of mastication, tensor veli palatini, tensor tympani & anterior belly of digastric, through motor nucleus of trigeminal.
Thus, trigeminal nerve has four nuclei: 3 sensory & 1 motor.
THE TRIGEMINAL GANGLION (GASSERION GANGLION or SEMILUNAR GANGLION):
- Lies in a dural pouch, the Cavum trigeminale (MECKEL’S CAVE) lodged in trigeminal impression close to petrous apex.
- Peripheral process of pseudounipolar neurons of ganglion form the three division of nerves & central process of these neurons form the sensory root of trigeminal.
- Blood supply of ganglion is from: Internal carotid artery, middle meningeal artery, accessory meningeal artery & meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery.
ASSOCIATED ROOTS AND BRANCHES:
- The central processes of the ganglion cells form the large sensory root of the trigeminal nerve ,which is attached to pons at its junction with the middle cerebellar peduncle.
- The small motor root of the trigeminal nerve is attached to the pons superomedialy to the sensory root.
- It passes under the ganglion from its medial to the lateral side and joins the mandibular nerve at the foramen ovale.
RELATIONS:
- MEDIALLY- Internal carotid artery & posterior part of cavernous sinus
- LATERALLY-Middle meningeal artery
- SUPERIORLY- Parahippocampal Gyrus
- INFERIORLY-Motor root of trigeminal nerve, greater petrosal nerve, apex of the petrous temporal bone & foramen lacerum
BRANCHES:
|
Branches |
Functional Components |
Cells of Origin / Termination |
Cranial Exit |
Distribution and Functions |
|
Ophthalmic division (CN V1) |
General sensory |
Trigeminal ganglion/spinal, principal and mesencephalic nucleus of CN V |
Superior orbital Fissure |
Sensation from cornea, skin of forehead, scalp, eyelids, nose, and mucosa of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses |
|
Maxillary division (CN V2) |
Foramen rotundum |
Sensation from skin of face over maxilla including upper lip, maxillary teeth, mucosa of nose, maxillary sinuses, and palate |
||
|
Mandibular division (CN V3) |
FORAMEN OVALE | |||
|
Branchial motor |
Trigeminal motor nucleus |
Motor to muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor veli palatini, andtensor tympani |
Exam Question
- Spinal nuclei is nuclei of trigeminal nerve.
- Mesencephalic nuclei of trigeminal nerve give sensory supply to massetric muscle.
- The third branch of trigeminal nuclei emerges from foramen ovale.
- Sensation from skin of face is carried by trigeminal nerve fibers from mesencephalic nucleus.
- The third branch of trigeminal nerve gives motor supply.
- Corneal reflex is due to trigeminal nerve innervation.
- Afferent component in corneal reflex is mediated by – TRIGEMINAL NERVE (OPHTHALMIC BRANCH).
- Efferent component in corneral reflex mediated by- FACIAL NERVE.
- CORNEAL REFLEX & JAW REFLEX are lost in trigeminal nerve injury.
- Unilateral trigeminal Nerve injury is tested by elevation & lowering of jaw.
- Anterior belly of digastric muscle is supplied by 3rd division of trigeminal nerve.
- Tensor tympani muscle is supplied by 3rd division of trigeminal nerve.
- Blood supply of trigeminal ganglion is from: Internal carotid artery, middle meningeal artery, accessory meningeal artery & meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery.