Type Iv Hypersensitivity
Introduction
- Cell-Mediated) Reactions/Delayed-type hypersensitivity/antibody-independent
- Involve reactions by memory cells.
- First contact sensitizes person.
- Subsequent contacts elicit a reaction.
- Reactions are delayed by one or more days (delayed type hypersensitivity).
- Delay is due to migration of macrophages and T cells to site of foreign antigens.
- Reactions are frequently displayed on the skin: itching, redness, swelling, pain.
- Tuberculosis skin test
- Poison ivy
- Metals
- Latex in gloves and condoms (3% of health care workers)
Peak action time
- after 24 hours
- Anaphylactic shock may occur
Initiated by
- activated T-lymphocytes.
Includes
- Delayed type hypersensitivity – mediated by CD-4 T cells.
- T-cell mediated cytotoxicity – mediated by CD8- T cells.
Delayed type hypersensitivity
- CD-4 T cells and macrophages are primarily involved
- Mechanism of defence against various intracellular pathogens
- mycobacteria
- fungi
- certain parasites.
- Pathophysiology
- Characterized by formation of granuloma
- a localized mass that contains activated macrophages (epitheloid) cells
- surrounded by collar of lymphocytes and giant cells.
- It is also called granulomatous inflammation.
- Antigen presenting cell comes in contact with naive CD-4 T cells
- Naive CD-4 T cells recognize these peptide antigens in association with MHC – II and differentiate in to T4-1 cells.
- Expression of delayed hypersensitivity largely depends on the cytokines secreted by T4-1 cells.
T-cell mediated cytotoxicity
- In this type of hypersensitivity, cytotoxic T cells kill virus infected or tumor cells.
Examples
- Tuberculin test
- Lepromin test
- Fairleys (Schistosomiasis) test
- Frie’s (LGV) test
- Granulomatous inflammation
- Contact dermatitis
- Defence against intracellular pathogen
- Type I lepra reaction
- Graft rejection
- Resistance to virus infection
- Reaction against tumour cells
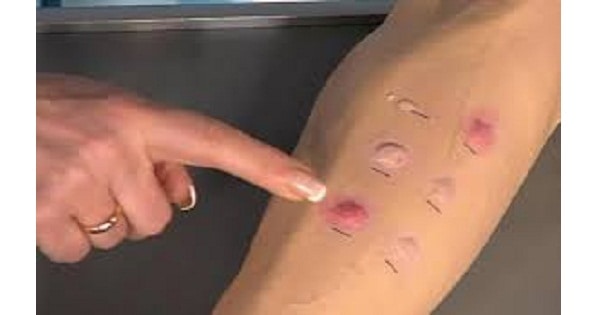
Type IV hypersensitivity Test
- Injection is given intradermally on the flexor aspect of the forearm.
- The site is examined after 48-72 hours.
- Induration of greater than 10 mm is considered as positive.
- Examples → Tuberculin test, Lepromin test
Exam Question
Introduction
- Cell-Mediated) Reactions/Delayed-type hypersensitivity/antibody-independent
- Involve reactions by memory cells.
- Reactions are delayed by one or more days (delayed type hypersensitivity).
- Delay is due to migration of macrophages and T cells to site of foreign antigens.
- Reactions are frequently displayed on the skin: itching, redness, swelling, pain.
Peak action time
- after 24 hours
Initiated by
- activated T-lymphocytes.
Includes
- Delayed type hypersensitivity – mediated by CD-4 T cells.
- T-cell mediated cytotoxicity – mediated by CD8- T cells.
Examples
- Tuberculin test
- Lepromin test
- Fairleys (Schistosomiasis) test
- Frie’s (LGV) test
- Granulomatousinflammation
- Contact dermatitis
- Defence against intracellular pathogen
- Type I lepra reaction
- Graft rejection
- Resistance to virus infection
- Reaction against tumour cells
Type IV hypersensitivity Test
- Injection is given intradermally on the flexor aspect of the forearm.
- The site is examined after 48-72 hours.
- Induration of greater than 10 mm is considered as positive.
- Examples → Tuberculin test, Lepromin test
Don’t Forget to Solve all the previous Year Question asked on Type Iv Hypersensitivity