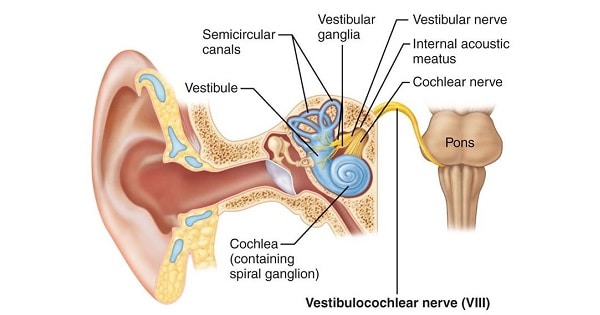
VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR (VIII) NERVE
| A | Medial lemniscus | |
| B | Lateral lemniscus | |
| C | Lateral geniculate body | |
| D | Medial geniculate body |
| A | Medial lemniscus | |
| B | Lateral lemniscus | |
| C | Lateral geniculate body | |
| D | Medial geniculate body |
Medial geniculate body
All of the following are concerned with auditory pathway except:
| A |
Trapezoid body |
|
| B |
Medial geniculate body |
|
| C |
Genu of internal capsule |
|
| D |
Lateral lemniscus |
All of the following are concerned with auditory pathway except:
| A |
Trapezoid body |
|
| B |
Medial geniculate body |
|
| C |
Genu of internal capsule |
|
| D |
Lateral lemniscus |
Ans. C Genu of internal capsule
- Organ of Corti is the sense organ of hearing and is situated on the basilar membrane.
- The actual sensory receptors in the organ of Corti are two specialized types of nerve cells k/a hair cells.
- Inner hair cells – single layer
- Outer hair cells – 3 or 4 layers
- The nerve fibers stimulated by the hair cells lead to the’spiral ganglion of Corti’which lies in the modiolus (center) of the cochleA.
- The spiral ganglia has bipolar cells – Its dendrites innervate the hair cells whereas the axons form the cochlear division of CN VIII and end in the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei located in the upper part of medullA.
Auditory Pathway
- All the fibres from the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei synapse (kla Trapezoid body) and the 2° order neurons pass mainly to the opposite side of the brainstem to terminate in the superior olivary nucleus
- A few 2° order fibers pass to the superior olivary nucleus on the same side
- From the superior olivary nucleus, the auditory pathway passes upward through the lateral lemniscus
- Some of the fibers terminate in the nucleus of the lateralleminiscus but many bypass this nucleus and travel on to the ‘inferior colliculus’, where all or almost all fibers do synapse.
- From there, the pathway passes to the medial geniculate nucleus, where all fibers synapse.
- Finally the pathway proceeds by way of auditory radiation to auditory cortex, located mainly in the superior gyrus of temporal bone.
Note
In short pathway of hearing is:
Organ of Corti
↓
Spiral ganglion
↓
Dorsal/ventral cochlear nuclei
↓
(Trapezoid body)
↓
Superior olivary nucleus
↓
Lateral lemniscus
↓
Inferior colliculus
↓
Medial geniculate body
↓
Auditory cortex.
Crossing over of the fibers from both sides occurs at 3 places in the brain.
- At the trapezoid body
- In the commissure between the 2 nuclei of lateral lemnisci
- In the commissure connecting the two inferior colliculi
Auditory transmission is via :
| A |
Lateral lemniscus |
|
| B |
Medial lemniscus |
|
| C |
Lateral geniculate body |
|
| D |
Frontal cortex |
Auditory transmission is via :
| A |
Lateral lemniscus |
|
| B |
Medial lemniscus |
|
| C |
Lateral geniculate body |
|
| D |
Frontal cortex |
A i.e. Lateral leminiscus
I. Auditory pathway: SC-SLIM-41,42
II. S– Spiral ganglia (cochlea)
III. C– Cochlear nuclei (ponto-medullary junction)
IV. S-Superior olivary nucleus (pons)
V. L-Lateral lemniscus (brain stem)
VI. I-Inferior colliculus (mid-brain)
VII. M-Medial geniculate body (meta-thalamus)
VIII. 41,42 – Brodmann area (cerebral cortex)
Trapezoid body is associated with
| A |
Auditory pathway |
|
| B |
Visual pathway |
|
| C |
Extrapyramidal system |
|
| D |
Pyramidal system |
Trapezoid body is associated with
| A |
Auditory pathway |
|
| B |
Visual pathway |
|
| C |
Extrapyramidal system |
|
| D |
Pyramidal system |
Cochlear nerve and pathway of hearing:
- Cochlear nerve is formed by axons of bipolar neurons of spiral ganglion (cochlear ganglion).
- Cochlear nerve carries impulse from sense organ (organ of corti) to dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei.
- The auditory pathway is as follows:
Auditory pathway ← Auditory radiation ← Medial geniculate body ← Inferior colliculus ← Lateral lemniscus
↑
Hair cells of organ of corti (in cochlea)→Spinal ganglion→Cochlear Nerve→Ventral & dorsal cochlear nuclei→Trapezoid body→Superior olivary complex
Scala tympani is supplied by which of the following nerve:
| A |
Abducent nerve |
|
| B |
Facial nerve |
|
| C |
Vestibulocochlear nerve |
|
| D |
Glossopharyngeal nerve |
Scala tympani is supplied by which of the following nerve:
| A |
Abducent nerve |
|
| B |
Facial nerve |
|
| C |
Vestibulocochlear nerve |
|
| D |
Glossopharyngeal nerve |
Vestibulo–cochlear nerve comprises of hearing and vestibular parts
Scala tympani
- It is one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the cochlear labyrinth of the ear.
- It is separated from the scala media by the basilar membrane, and it extends from the round window to the helicotrema, where it continues as scala vestibuli.
- The purpose of the perilymph-filled scala tympani and scala vestibuli is to transduce the movement of air that causes the tympanic membrane and the ossicles to vibrate, to movement of liquid and the basilar membrane.
- The movement of the basilar membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the sterocilia to bend.
- They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve.
- This produces the sensation of sound.
All are involved in Auditory pathway except
| A |
Cochlear nerve |
|
| B |
Vestibular nerve |
|
| C |
Trapezoid body |
|
| D |
Inferior colliculus |
All are involved in Auditory pathway except
| A |
Cochlear nerve |
|
| B |
Vestibular nerve |
|
| C |
Trapezoid body |
|
| D |
Inferior colliculus |
Ans. is ‘b’ i.e., Vestibular nerve
All are involved in auditory pathway except ‑
| A |
Trapezoid body |
|
| B |
Lateral geniculate body |
|
| C |
Inferior colliculus |
|
| D |
Superior olivary complex |
All are involved in auditory pathway except ‑
| A |
Trapezoid body |
|
| B |
Lateral geniculate body |
|
| C |
Inferior colliculus |
|
| D |
Superior olivary complex |
Ans. is ‘b’ i.e., Lateral geniculate body